4. Core software functions of BMS
l Measurement function
(1) Basic information measurement: monitoring battery voltage, current signal, and battery pack temperature. The most basic function of the battery management system is to measure the voltage, current, and temperature of battery cells, which is the basis of all top-level calculations and control logic of the battery management system.
(2) Insulation resistance detection: The entire battery system and high-voltage system need to be tested for insulation by the battery management system.
(3) High-voltage interlock detection (HVIL): used to confirm the integrity of the entire high-voltage system. When the integrity of the high-voltage system circuit is damaged, safety measures are activated.
l Estimation function
(1) SOC and SOH estimation: the core and most difficult part
(2) Balancing: adjust the SOC x capacity imbalance between monomers through a balancing circuit.
(3) Battery power limitation: the input and output power of the battery are limited at different SOC temperatures.
l Other functions
(1) Relay control: including main +, main-, charging relay +, charging relay -, pre-charging relay
(2) Thermal control
(3) Communication function
(4) Fault diagnosis and alarm
(5) Fault-tolerant operation
5. Core software functions of BMS
l Measurement function
(1) Basic information measurement: monitoring battery voltage, current signal, and battery pack temperature. The most basic function of the battery management system is to measure the voltage, current, and temperature of battery cells, which is the basis of all top-level calculations and control logic of the battery management system.
(2) Insulation resistance detection: The entire battery system and high-voltage system need to be tested for insulation by the battery management system.
(3) High-voltage interlock detection (HVIL): used to confirm the integrity of the entire high-voltage system. When the integrity of the high-voltage system circuit is damaged, safety measures are activated.
l Estimation function
(1) SOC and SOH estimation: the core and most difficult part
(2) Balancing: adjust the SOC x capacity imbalance between monomers through a balancing circuit.
(3) Battery power limitation: the input and output power of the battery are limited at different SOC temperatures.
l Other functions
(1) Relay control: including main +, main-, charging relay +, charging relay -, pre-charging relay
(2) Thermal control
(3) Communication function
(4) Fault diagnosis and alarm
(5) Fault-tolerant operation
6. BMS software architecture
l High and low voltage management
When normally powered on, the BMS is awakened by the VCU via a hard line or CAN signal of 12V. After the BMS completes self-check and enters standby, the VCU sends a high-voltage command, and the BMS controls the closing of the relay to complete the high-voltage connection. When powered off, the VCU sends a low-voltage command and then disconnects the 12V wake-up. When the gun is inserted for charging in the power-off state, it can be awakened by the CP or A+ signal.
l Charging management
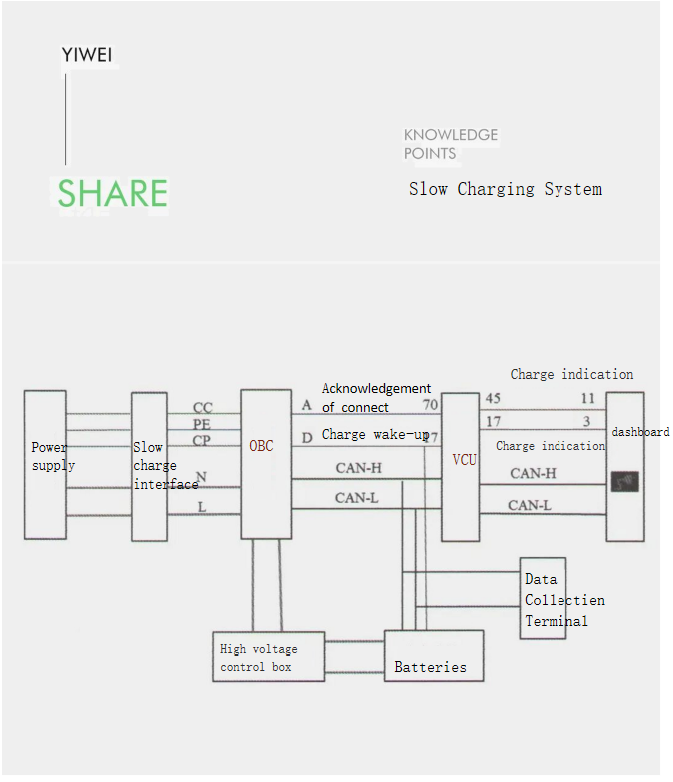
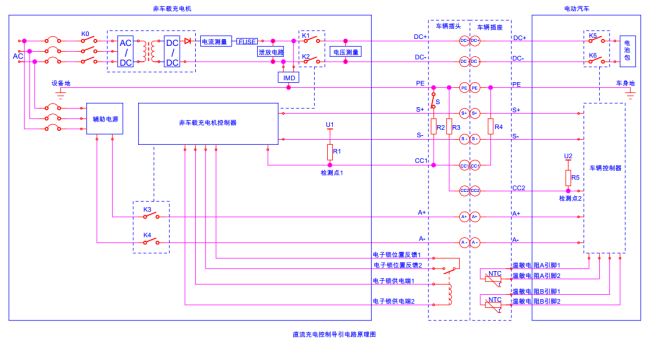
(1) Slow charging
Slow charging is to charge the battery with direct current converted from alternating current by the on-board charger of the charging pile (or 220V power supply). The charging pile specifications are generally 16A, 32A, and 64A, and it can also be charged through a household power supply. The BMS can be awakened by the CC or CP signal, but it should be ensured that it can sleep normally after charging is completed. The AC charging process is relatively simple and can be developed in accordance with detailed national standards.
(2) Fast charging
Fast charging is to charge the battery with direct current output by the DC charging pile, which can achieve 1C or even higher charging rate. Generally, 80% of the battery can be charged in 45 minutes. It can be awakened by the auxiliary power source A+ signal of the charging pile.
l Estimation function
(1) SOP (State of Power) mainly obtains the current battery’s available charging and discharging power by looking up tables through temperature and SOC. The VCU determines how the entire vehicle is used based on the power value sent.
(2) SOH (State of Health) mainly characterizes the current health status of the battery, with a value between 0-100%. It is generally considered that the battery cannot be used after it drops below 80%.
(3) SOC (State of Charge) belongs to the core control algorithm of the BMS, which characterizes the current remaining capacity status. It is mainly based on the ampere-hour integral method and the EKF (extended Kalman filter) algorithm, combined with correction strategies (such as open-circuit voltage correction, full charge correction, end-of-charge correction, capacity correction under different temperatures and SOH, etc.).
(4) SOE (State of Energy) algorithm is not widely developed by domestic manufacturers or uses relatively simple algorithms to obtain the ratio of the remaining energy under the current state to the maximum available energy. This function is mainly used for estimating the remaining cruising range.
l Fault diagnosis
Different fault levels are distinguished according to the different performance of the battery, and different processing measures are taken by the BMS and VCU under different fault levels, such as warnings, power limitation, or direct disconnection of high voltage. Faults include data acquisition and rationality faults, electrical faults (sensors and actuators), communication faults, and battery status faults, etc.
1. Core software functions of BMS
l Measurement function
(1) Basic information measurement: monitoring battery voltage, current signal, and battery pack temperature. The most basic function of the battery management system is to measure the voltage, current, and temperature of battery cells, which is the basis of all top-level calculations and control logic of the battery management system.
(2) Insulation resistance detection: The entire battery system and high-voltage system need to be tested for insulation by the battery management system.
(3) High-voltage interlock detection (HVIL): used to confirm the integrity of the entire high-voltage system. When the integrity of the high-voltage system circuit is damaged, safety measures are activated.
l Estimation function
(1) SOC and SOH estimation: the core and most difficult part
(2) Balancing: adjust the SOC x capacity imbalance between monomers through a balancing circuit.
(3) Battery power limitation: the input and output power of the battery are limited at different SOC temperatures.
l Other functions
(1) Relay control: including main +, main-, charging relay +, charging relay -, pre-charging relay
(2) Thermal control
(3) Communication function
(4) Fault diagnosis and alarm
(5) Fault-tolerant operation
2. BMS software architecture
l High and low voltage management
When normally powered on, the BMS is awakened by the VCU via a hard line or CAN signal of 12V. After the BMS completes self-check and enters standby, the VCU sends a high-voltage command, and the BMS controls the closing of the relay to complete the high-voltage connection. When powered off, the VCU sends a low-voltage command and then disconnects the 12V wake-up. When the gun is inserted for charging in the power-off state, it can be awakened by the CP or A+ signal.
l Charging management
(1) Slow charging
Slow charging is to charge the battery with direct current converted from alternating current by the on-board charger of the charging pile (or 220V power supply). The charging pile specifications are generally 16A, 32A, and 64A, and it can also be charged through a household power supply. The BMS can be awakened by the CC or CP signal, but it should be ensured that it can sleep normally after charging is completed. The AC charging process is relatively simple and can be developed in accordance with detailed national standards.
(2) Fast charging
Fast charging is to charge the battery with direct current output by the DC charging pile, which can achieve 1C or even higher charging rate. Generally, 80% of the battery can be charged in 45 minutes. It can be awakened by the auxiliary power source A+ signal of the charging pile.
l Estimation function
(1) SOP (State of Power) mainly obtains the current battery’s available charging and discharging power by looking up tables through temperature and SOC. The VCU determines how the entire vehicle is used based on the power value sent.
(2) SOH (State of Health) mainly characterizes the current health status of the battery, with a value between 0-100%. It is generally considered that the battery cannot be used after it drops below 80%.
(3) SOC (State of Charge) belongs to the core control algorithm of the BMS, which characterizes the current remaining capacity status. It is mainly based on the ampere-hour integral method and the EKF (extended Kalman filter) algorithm, combined with correction strategies (such as open-circuit voltage correction, full charge correction, end-of-charge correction, capacity correction under different temperatures and SOH, etc.).
(4) SOE (State of Energy) algorithm is not widely developed by domestic manufacturers or uses relatively simple algorithms to obtain the ratio of the remaining energy under the current state to the maximum available energy. This function is mainly used for estimating the remaining cruising range.
l Fault diagnosis
Different fault levels are distinguished according to the different performance of the battery, and different processing measures are taken by the BMS and VCU under different fault levels, such as warnings, power limitation, or direct disconnection of high voltage. Faults include data acquisition and rationality faults, electrical faults (sensors and actuators), communication faults, and battery status faults, etc.
Contact us:
yanjing@1vtruck.com +(86)13921093681
duanqianyun@1vtruck.com +(86)13060058315
liyan@1vtruck.com +(86)18200390258
Post time: May-12-2023