In the hot summer or cold winter, the car air conditioning is essential for us car enthusiasts, especially when the windows fog up or frost over. The ability of the air conditioning system to quickly defog and defrost plays a crucial role in driving safety. For electric vehicles, which lack a fuel engine, they don’t have a heat source for heating, and the compressor doesn’t have the engine’s driving force to provide cooling. So how do pure electric vehicles provide air conditioning cooling and heating functions? Let’s find out.
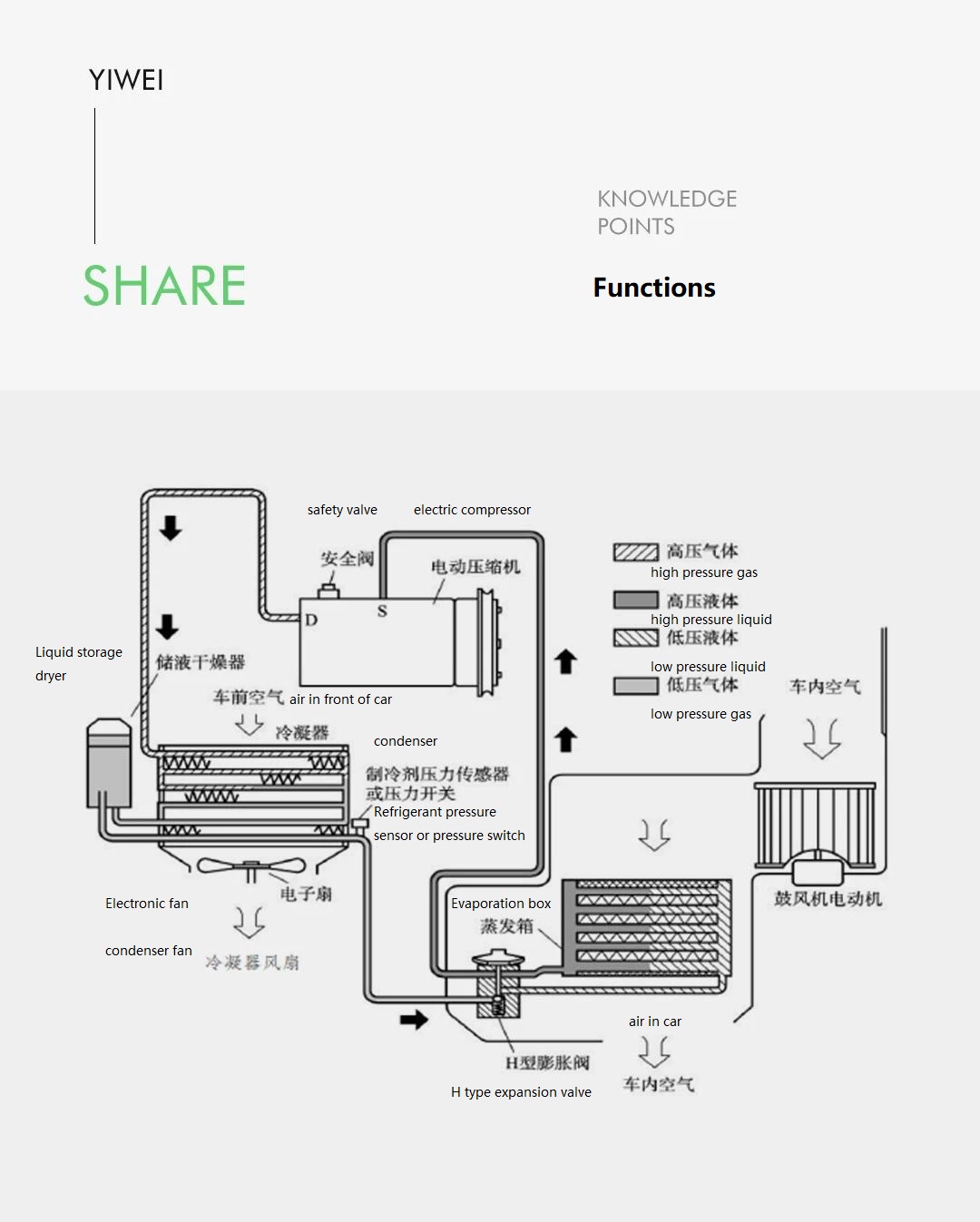
01 Components of the Air Conditioning Cooling System
The components of the air conditioning cooling system include: electric compressor, condenser, pressure sensor, electronic expansion valve, evaporator, air conditioning hard pipes, hoses, and control circuit.
Compressor:
It takes in low temperature and low-pressure gaseous refrigerant and compresses it into high-temperature and high-pressure liquid refrigerant gas. During compression, the state of the refrigerant remains unchanged, but the temperature and pressure continuously increase, forming superheated gas.
Condenser:
The condenser uses a dedicated cooling fan to dissipate the heat of the high-temperature and high-pressure refrigerant to the surrounding air, cooling down the refrigerant. In this process, the refrigerant changes from a gaseous state to a liquid state, and it is in a high-temperature and high-pressure state.
Expansion Valve:
The high-temperature and high-pressure liquid refrigerant passes through the expansion valve to throttle and reduce the pressure before entering the evaporator. The purpose of this process is to cool and depressurize the refrigerant and regulate the flow to control the cooling capacity. When the refrigerant passes through the expansion valve, it changes from a high-temperature, high-pressure liquid to a low-temperature, low-pressure liquid state.
Evaporator:
The low-temperature, low-pressure liquid refrigerant coming from the expansion valve absorbs a large amount of heat from the surrounding air in the evaporator. During this process, the refrigerant changes from a liquid to a low-temperature, low-pressure gas. This gas is then sucked in by the compressor for compression again.
From a cooling principle standpoint, the air conditioning system of electric vehicles is basically the same as that of traditional fuel-powered vehicles. The difference mainly lies in the driving method of the air conditioning compressor. In traditional fuel-powered vehicles, the compressor is driven by the engine’s belt pulley, while in electric vehicles, the compressor is controlled by electronic control to drive the motor, which in turn operates the compressor through the crankshaft.
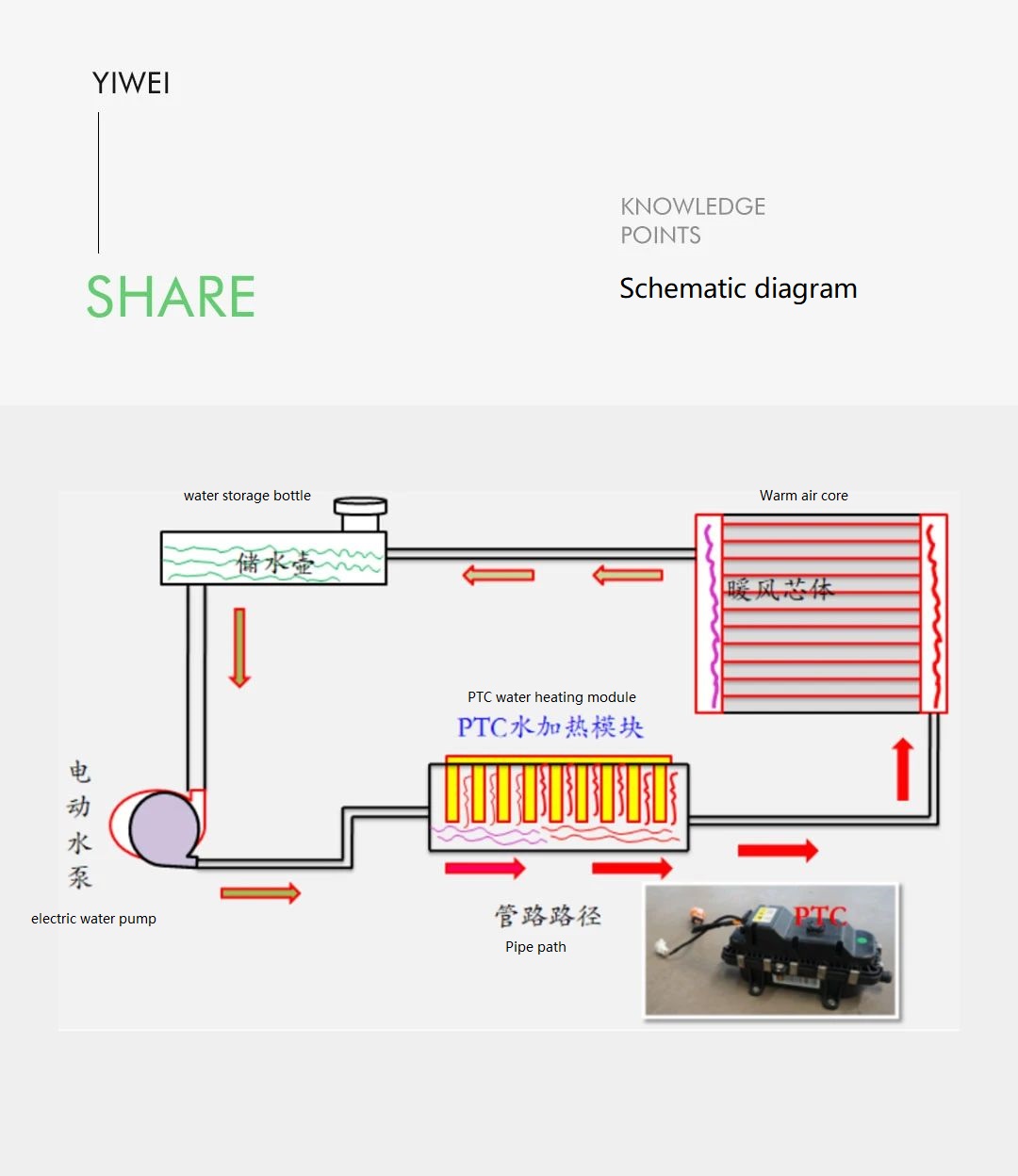
02 Air Conditioning Heating System
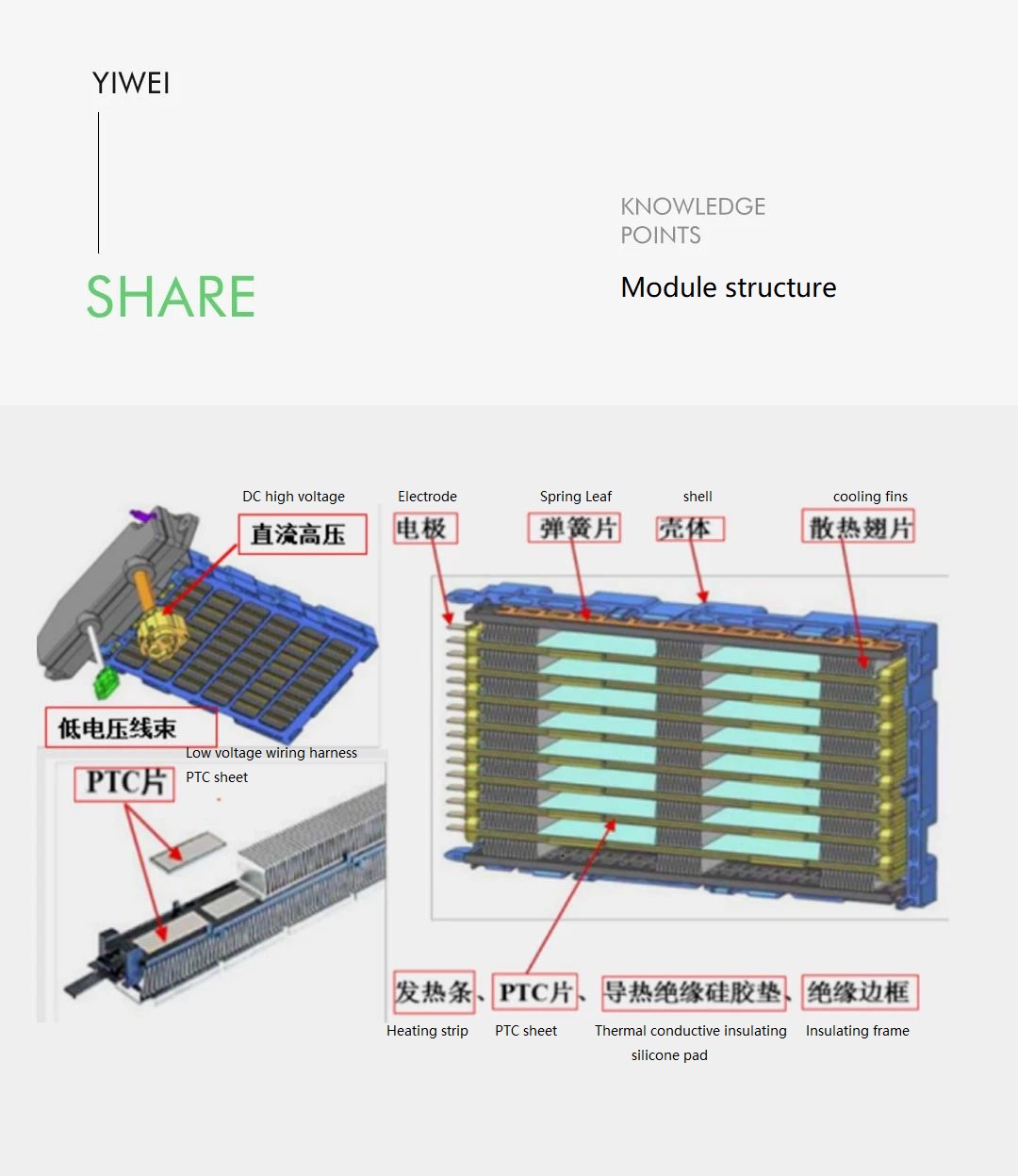
The heating source is mainly obtained through PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient) heating. Pure electric vehicles generally have two forms: PTC module for air heating and PTC module for water heating. PTC is a type of semiconductor thermistor, and its characteristic is that the resistance of the PTC material increases as the temperature rises. Under constant voltage, the PTC heater heats up quickly at low temperatures, and as the temperature rises, the resistance increases, the current decreases, and the energy consumed by the PTC decreases, thus maintaining a relatively constant temperature.
Internal Structure of Air Heating PTC Module:
It consists of a controller (including low voltage/high voltage drive module), high/low-pressure wire harness connectors, PTC heating resistive film, thermally conductive insulating silicone pad, and outer shell, as shown in the figure.
Air heating PTC module refers to directly installing the PTC at the core of the cabin’s warm air system. The cabin air is circulated by the blower and heated directly by the PTC heater. The heating resistive film inside the air heating PTC module is powered by high voltage and controlled by the VCU (Vehicle Control Unit).
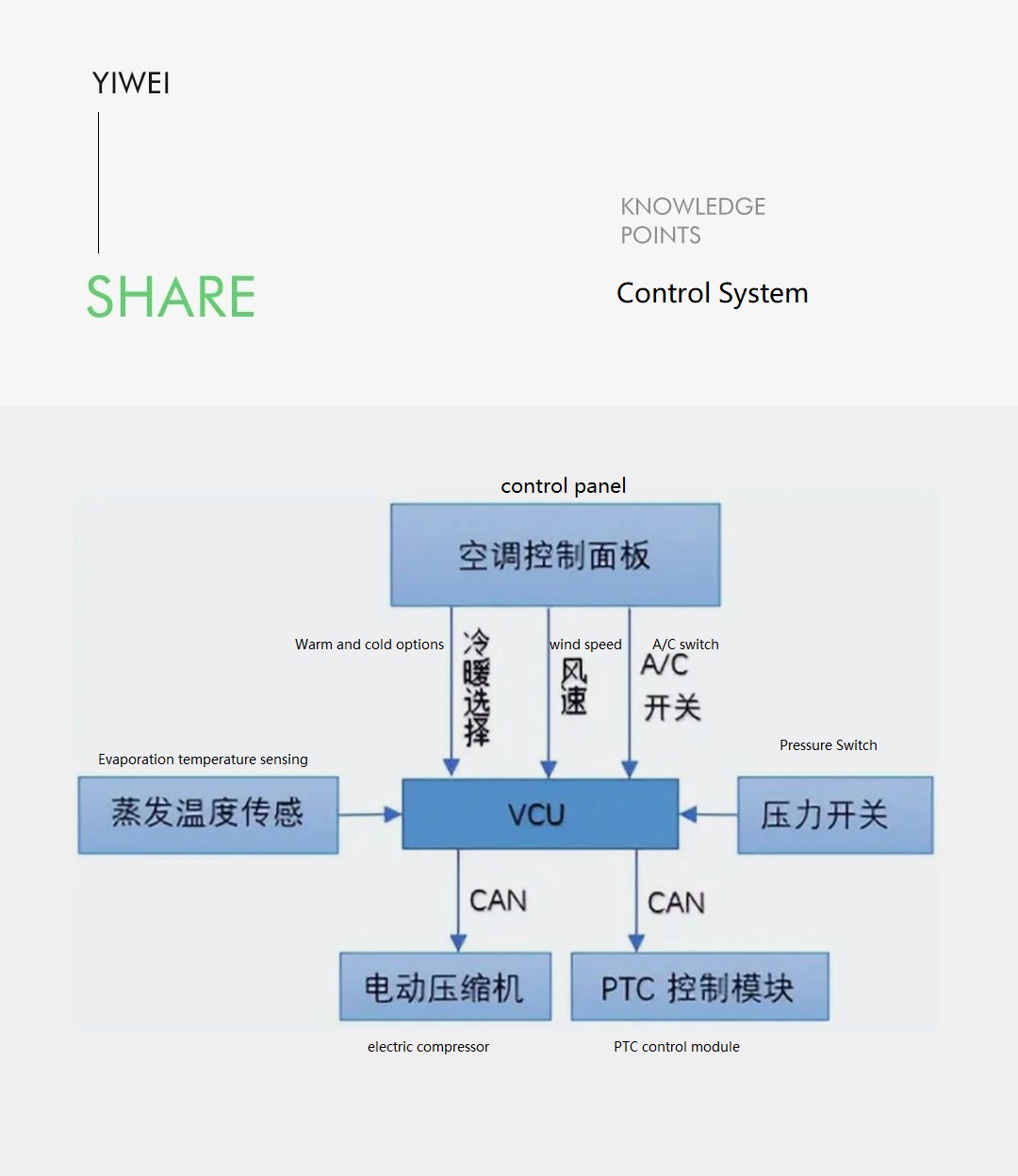
03 Control of the Electric Vehicle Air Conditioning System
The electric vehicle’s VCU collects signals from the A/C switch, A/C pressure switch, evaporator temperature, fan speed, and ambient temperature. After processing and calculation, it generates control signals, which are transmitted to the air conditioning controller via the CAN bus. The air conditioning controller controls the on/off of the high-voltage circuit of the air conditioning compressor, as shown in the figure.
That concludes the general introduction to the air conditioning system of electric vehicles. Did you find it helpful? Follow Yiyi New Energy Vehicles for more professional knowledge shared every week.
Contact us:
yanjing@1vtruck.com +(86)13921093681
duanqianyun@1vtruck.com +(86)13060058315
liyan@1vtruck.com +(86)18200390258
Post time: Sep-13-2023