With the active support of national policies in recent years, the popularity and application of new energy sanitation vehicles are expanding at an unprecedented rate. During the usage process, how to make pure electric sanitation vehicles more energy-efficient and cost-effective has become a common concern for many customers. We have summarized the following strategies to help users maximize vehicle energy efficiency and reduce costs.
Taking Chengdu as an example, based on the power grid load variations, the 24 hours of the day are divided into peak, flat, and valley periods, with different electricity tariffs applied to each period. According to big data analysis of the YIWEI 18-ton pure electric street sweeper (equipped with 231 kWh of battery capacity), the average daily charging amount is about 200 kWh. The charging cost during peak hours is approximately: 200 × 0.85 = 170 RMB, while the charging cost during valley periods is roughly: 200 × 0.23 = 46 RMB. (These calculations exclude charging station service fees and parking fees.)
By avoiding peak electricity usage periods, if the vehicle is charged during the valley period every day, about 124 RMB can be saved per day on electricity costs. Annually, this results in savings of: 124 × 29 × 12 = 43,152 RMB (based on 29 days of operation per month). Compared to traditional fuel-powered sweepers, the energy cost savings per year can exceed 100,000 RMB.
For rural sanitation and landscaping companies that are far from commercial charging stations, custom AC charging interfaces can be designed for smaller vehicles to charge during the valley period using household electricity, avoiding unnecessary energy loss when traveling back and forth to commercial charging stations.
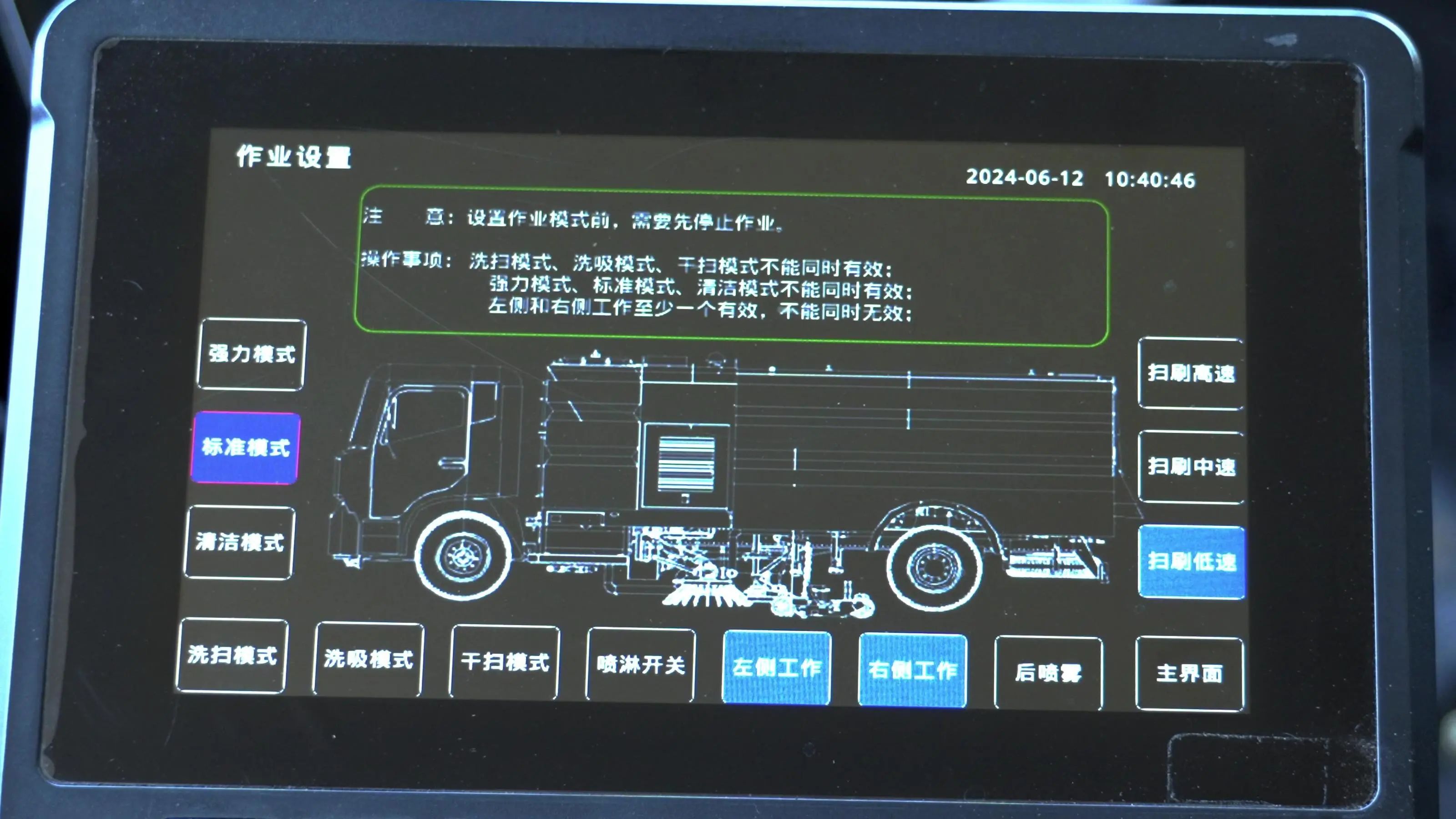
Based on the actual cleaning tasks, the cleaning intensity, speed, and other parameters should be adjusted to avoid energy waste caused by overwork. For example, the YIWEI 18-ton sweeper features three energy consumption modes: “Powerful,” “Standard,” and “Energy Saving.” When working in areas that require a higher level of cleanliness, the cleaning intensity can be appropriately reduced to save energy.
Drivers should be trained in energy-saving driving techniques, such as smooth starts, maintaining a steady speed, and avoiding rapid acceleration or hard braking. When not in operation, the vehicle should be maintained at an economical speed of 40-60 km/h to effectively reduce energy consumption.
Use air conditioning equipment judiciously: turning on the air conditioning for cooling or heating will increase electricity consumption. In the fall and early winter when temperatures are comfortable, the use of air conditioning can be minimized. Additionally, reducing unnecessary items inside the vehicle can help reduce weight, improving energy efficiency. It is also important to maintain proper tire pressure, as insufficient tire pressure increases rolling resistance and leads to higher energy consumption.
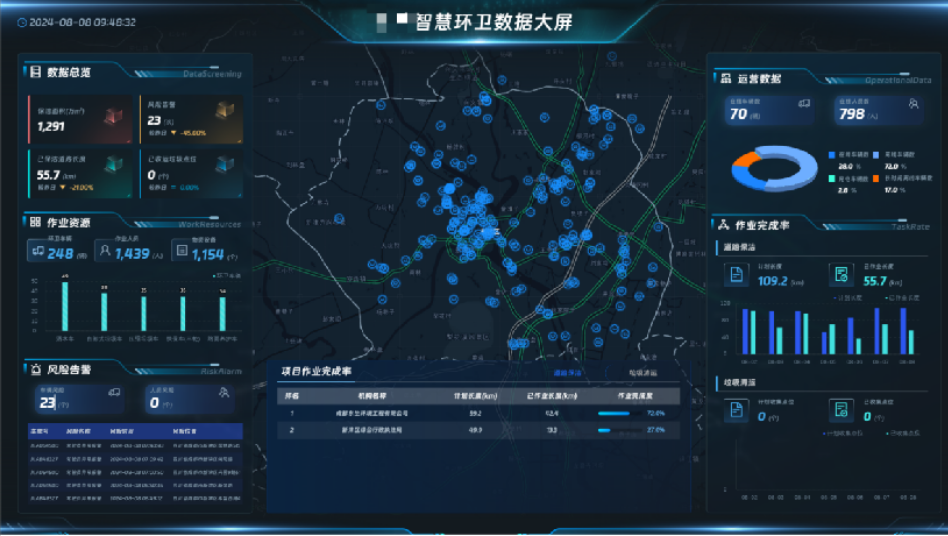
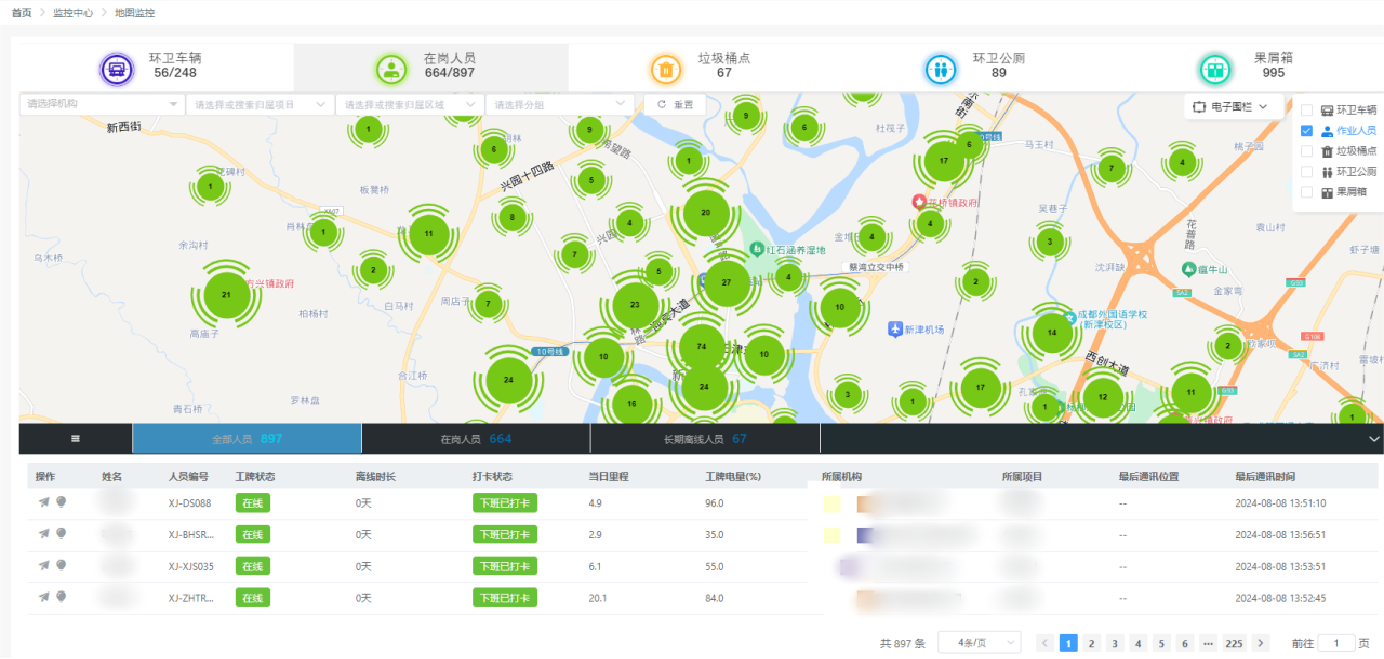
Advanced intelligent scheduling systems can also be utilized. For example, the YIWEI self-developed smart sanitation platform can dynamically adjust the work plan and optimize the cleaning route based on factors such as work area, real-time road conditions, and waste distribution, thereby reducing unnecessary driving and lowering energy consumption.
In conclusion, optimizing the operational costs, particularly the electricity consumption, of new energy sanitation vehicles is key to improving overall operational efficiency and economic benefits. As technology continues to advance and policies provide ongoing support, the future of new energy sanitation vehicles looks even brighter, offering a cleaner, more beautiful, and sustainable blueprint for both urban and rural development.
Post time: Nov-11-2024