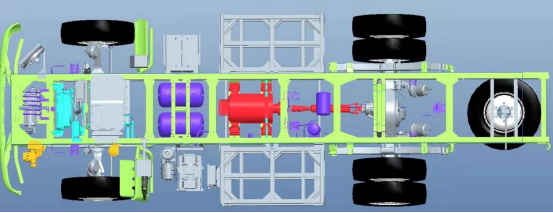
New energy vehicles have three key technologies that traditional vehicles do not possess. While traditional vehicles rely on their three major components, for pure electric vehicles, the most crucial part is their three electric systems: the motor, the motor controller unit (MCU), and the battery.
- Motor:
Commonly referred to as the "engine," the motor can be categorized into three types for electric vehicles:
DC Motor: This uses a brushed DC motor controlled by a chopper circuit.
- Advantages: Simple structure and easy control. It was one of the earliest drive systems used in electric vehicles.
- Disadvantages: Low efficiency and short lifespan.
AC Induction Motor: It utilizes a design with coils and an iron core. When electric current flows through the coils, a magnetic field is produced, which changes direction and magnitude with the current.
- Advantages: Relatively lower cost.
- Disadvantages: High energy consumption. Widely used in industrial applications.
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM): It operates based on the principle of electromagnetism. When energized, the motor's coils generate a magnetic field, and due to the repulsion of internal magnets, the coils start to rotate.
- Our company uses PMSM motors, known for their high efficiency, compact size, lightweight, and precise control.
- Electronic Control Unit (ECU):
The ECU for electric vehicles connects to the power battery in the front and the drive motor in the rear. Its role is to convert direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) and respond to control signals from the vehicle's controller to regulate the required speed and power.
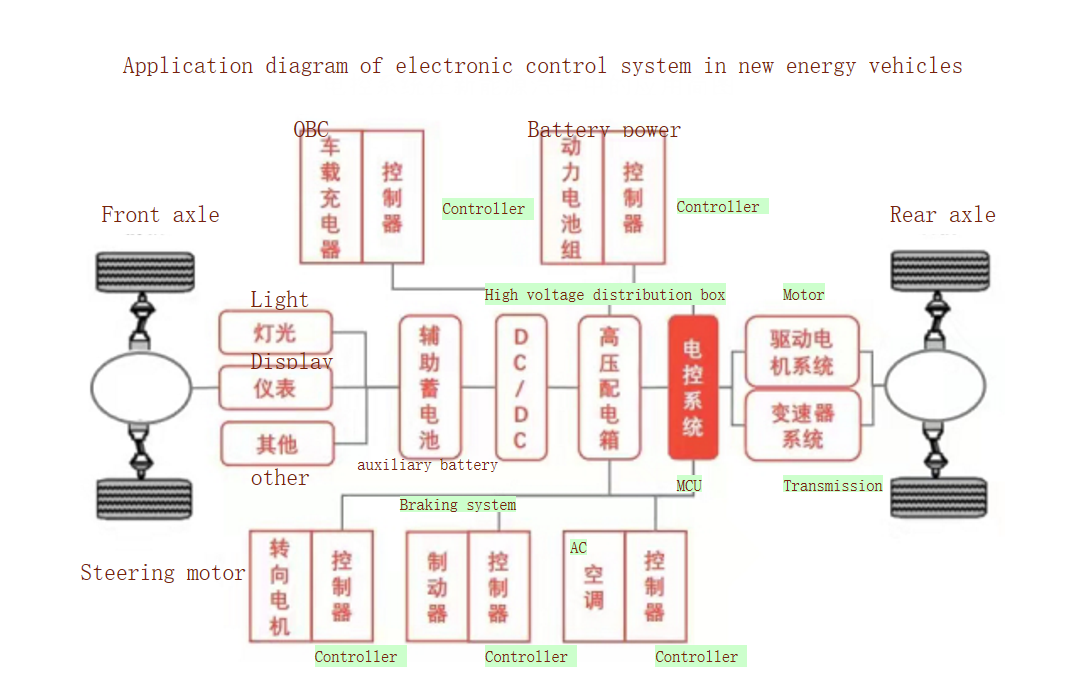
- Battery:
The heart of a new energy vehicle is the power battery. There are generally five types of batteries available on the market:
Lead-Acid Battery:
- Advantages: Low cost, good performance in low temperatures, and high cost-effectiveness.
- Disadvantages: Low energy density, short lifespan, large size, and poor safety.
- Usage: Due to low energy density and limited lifespan, lead-acid batteries are typically used in low-speed vehicles.
Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Battery:
- Advantages: Low cost, mature technology, long lifespan, and durability.
- Disadvantages: Low energy density, large size, low voltage, and susceptible to memory effect. Contains heavy metals, which can cause environmental pollution when disposed of.
- Usage: Performs better than lead-acid batteries.
Lithium Manganese Oxide (LiMn2O4) Battery:
- Advantages: Low cost, good safety and low-temperature performance for positive electrode materials.
- Disadvantages: Relatively unstable materials, prone to decomposition and gas generation, rapid degradation of cycle life, poor performance at high temperatures, and relatively short lifespan.
- Usage: Mainly used in medium to large-sized battery cells for power batteries, with a nominal voltage of 3.7V.
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) Battery:
- Advantages: Excellent thermal stability, safety, low cost, and long lifespan.
- Disadvantages: Low energy density, sensitive to low temperatures.
- Usage: At temperatures around 500-600°C, the internal chemical components begin to decompose. It does not burn or explode when punctured, short-circuited, or exposed to high temperatures. It also has a longer lifespan. However, its driving range is generally limited. It is not suitable for charging in colder temperatures in northern regions.
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) Battery:
- Advantages: High energy density, long cycle life, and excellent performance in low temperatures.
- Disadvantages: Insufficient stability at high temperatures.
- Usage: Suitable for pure electric vehicles with specific requirements for driving range. It is the mainstream direction and suitable for colder climates as the battery remains stable at low temperatures.
Our company utilizes lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries, which have a stable voltage platform, efficient energy utilization, and nearly no thermal runaway (thermal runaway temperature is above 800°C), ensuring high safety.
Currently, the momentum of domestic new energy vehicles in China is quite remarkable, driving rapid urban development through technology. I believe that by each of us at Yiwei persevering and working together, we can contribute to creating a better city. Through continuous innovation and practical applications, we can promote the development of the sanitation industry using new environmental technologies.
Contact us:
yanjing@1vtruck.com +(86)13921093681
duanqianyun@1vtruck.com +(86)13060058315
liyan@1vtruck.com +(86)18200390258
Post time: Aug-31-2023